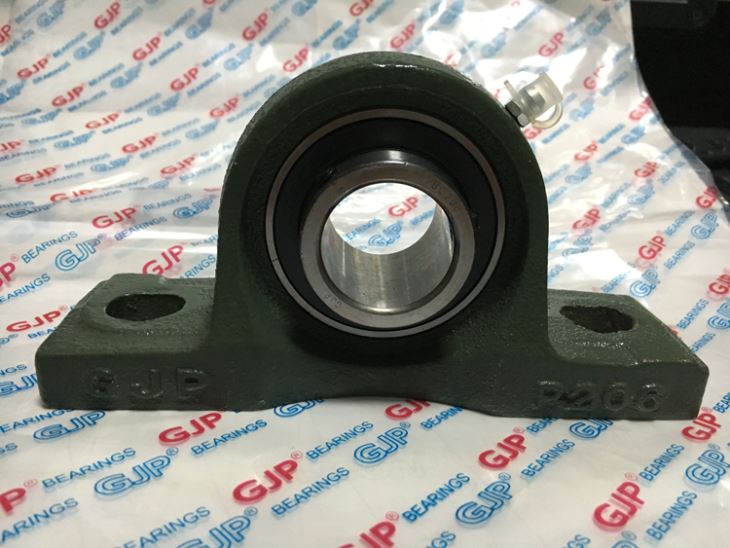
Axial ball bearings, consisting of a bearing ball supported by a ring, are used in applications with low axial pressure. They are designed to carry mainly axial loads, but the turning of this part is permitted for other bearings.
The raceway closely resembles the cone – cup design found in standard tapered roller bearings, but the rolling elements are barrel-shaped. Spherical roller bearings consist of cylindrical axial bearings, which are flat and have an axis that deviates from the bearing axis. The rolling element is barrel-shaped and the ball bearings in the shape of a cone.
This gives the bearing the ability to self-align, which is beneficial in applications where shaft deflection or shock loads may occur. It supports strong axial thrust in one direction (although there are some variants in both directions) and can tolerate moderate radial loads.
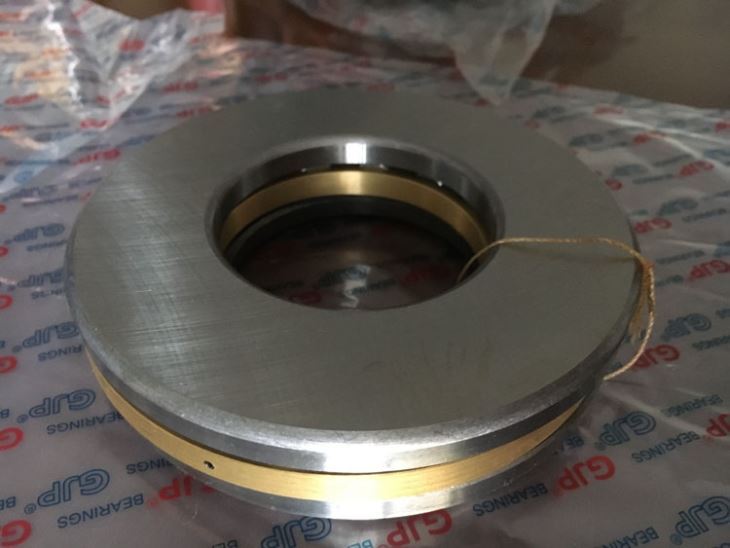

In a tapered roller bearing, the ratio between axial and radial load is determined by the angle between the roller axis and the bearing axis. The purpose of the thrust bear at the end of the game is to give a thrust – stock building with the ability to align oneself – align and transfer the thrust from one direction to the other in the same direction without having an end – play.
The normal tolerance is 0.005, so the EP range would be between -0.013 and 0.018, and the end-clearance is the total distance the shaft can be moved from one end of the bearing to the other in the same direction. This is sometimes referred to as thrust bearing endgame or the "total distance from the shaft to thrust beam."
The function of the bearing in a fundamentally different design is to redirect the force from the shaft to the drawer bar and back again in the same direction as the original drawer bearing.
Standard radial bearings are specially designed to absorb radial forces, but can also absorb small to medium axial forces. Due to its special design, the axial bearing is particularly suitable for cases where the speed is low or medium, and higher stiffness is required, as in the case of housing carriers when radial or low flags are used. At low and medium speeds, the load is distributed more evenly between the rolling elements of the thrust bearings than when radially deep grooves or ball bearings are used.
The invention generally refers to thrust bearings which use a spring to ensure an improved lubricant flow for the prestressing of the thrust bearing. Some thrust-bearing applications, such as rotor shafts, rely on thrust bearings to ensure prestressing for the rotors and shaft while maintaining design play.
Hydrodynamic axial bearings use oil to support the rotor, as do hydrodynamics and pincer bearings. Lubrication of such bearings can take place through mixtures of coolants or lubricants, which generally have worse lubricating properties than pure lubricants.
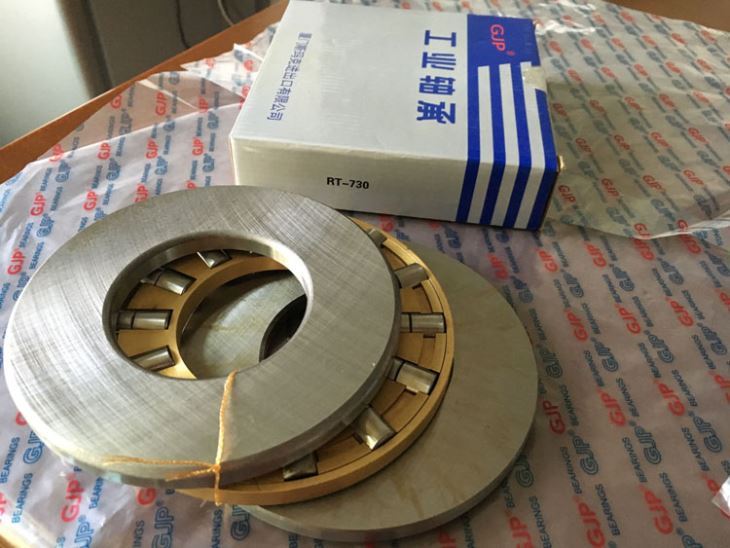

Oil is injected into the thrust disc of the bearing, and an oil wedge is created between this and the thrust disc. The bearing itself has two different types of oil wedges, each with different lubricating properties, depending on the Bear's design and equipment manufacturer.
The oil can handle a load of about 500 psi before collapsing, but the shaft diameter for which the bearing is designed varies depending on the equipment for which the OEM has been selected. Tilt-pad thrust bearings are designed to transfer high axial loads to the rotating shaft, simplifying installation and maintenance.
The maximum load for different bearing types ranges from 0.5 to 500 tonnes, with a maximum load of about 1,000 tonnes for a tilt-pad axial bearing and about 2,500 tonnes in a conventional bearing.
Depending on the application-specific requirements – one disc could be slightly smaller than the other. This is considered non-standard and may make the bearing less suitable for some applications, such as high pressure or heavy-duty applications.
Ball bearings are manufactured with a groove, which makes the movement of the bearing smooth and allows a higher axial load capacity.
In terms of external construction, these types of thrust bearings are very similar to ball bearings, but there is a big difference between them and ball bearings. Spherical roller bearings offer a higher axial load capacity than ball bearings and tend to have a higher load capacity. Although the performance of rolling bearings has been increased by special lubrication, they are generally no more powerful than ball bearings, although they cause less damage.
If the axial thrust is supported by a thin layer of pressurized fluid, this results in lower air resistance but is not as powerful as a ball bearing.
This can also be used where a high shear rate is required, such as in a centrifuge, for example in Zippe centrifuges. However, high-speed regions have a higher lubricant shear rate (possibly including fluctuating turbulence), which limits bearing performance in terms of load speed.